
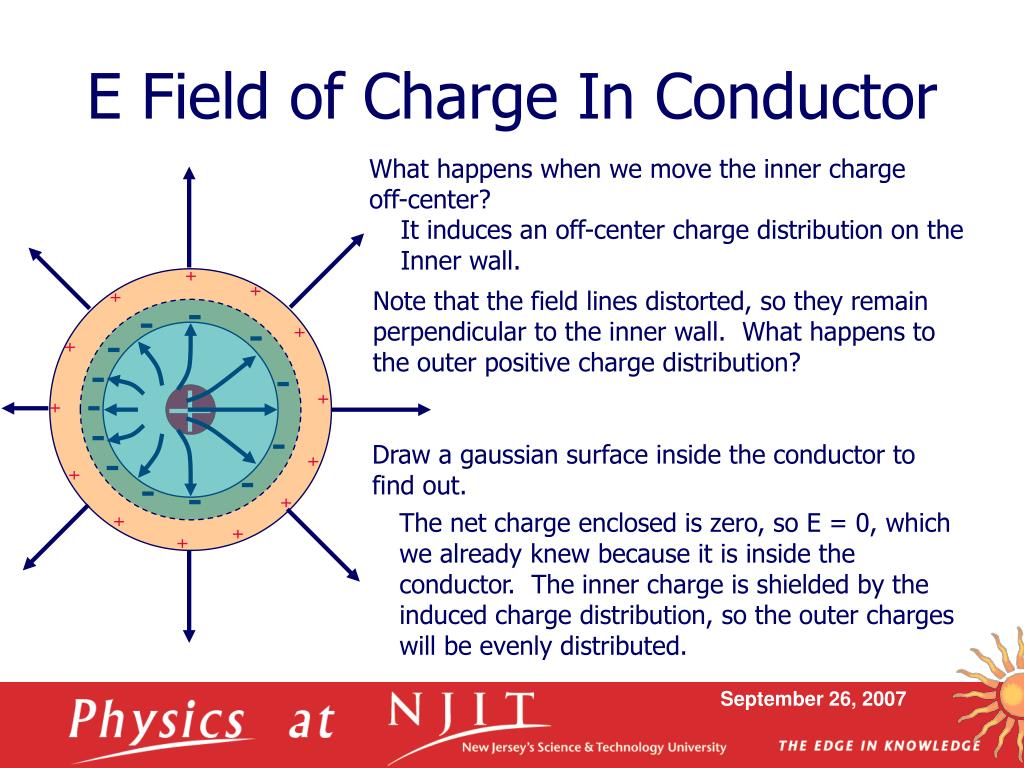
Derive an expression for electric field inside a solid nonconducting sphere of charge Q when the
Nonconductors or electrical insulators are materials which lack movable electric charges, and which therefore lack a low-resistance path for charge flow. When a difference in electrical potential is placed across a nonconductor, no free charges are exposed to the electric field, so no flow of charges appears, and an electric current cannot arise.

PPT L 23 Electricity & [1] PowerPoint Presentation ID6390016
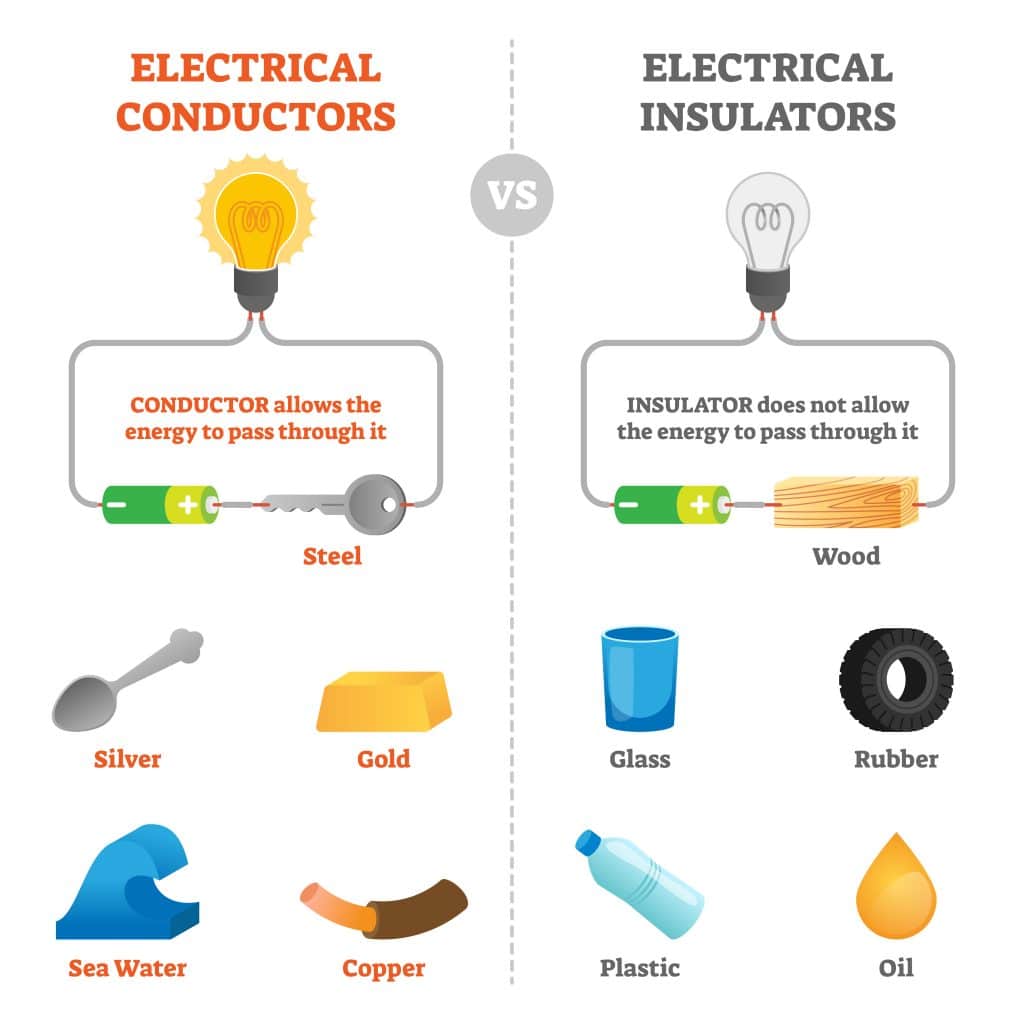
In physics electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge ( electric current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. The flow of negatively charged electrons generates electric current, positively charged holes, and positive or negative ions in.

6th grade. Electricity and
Home Science Physics Matter & Energy Conductors, insulators, and semiconductors Materials are classified as conductors, insulators, or semiconductors according to their electric conductivity. The classifications can be understood in atomic terms.

Electric Field due to charged Non Conducting Sphere, Non conducting sphere, Class 12 Physics
The main difference between Insulator and Non-Conductor is that an insulator is any substance that prohibits the transmission of heat, sound, or electricity. Whereas, non-conductor is any material that prohibits the transmission of electricity.
PPT Static Electricity and Electric Fields PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6072844
1. In electric circuits, a material that does not permit the flow of electrons through itself upon application of an electric field across itself. Note: Examples of nonconductors are dielectric materials, such as glass, plastic, rubber, and natural and synthetic fibers, such as cotton and nylon.
PPT Atomic Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1680708
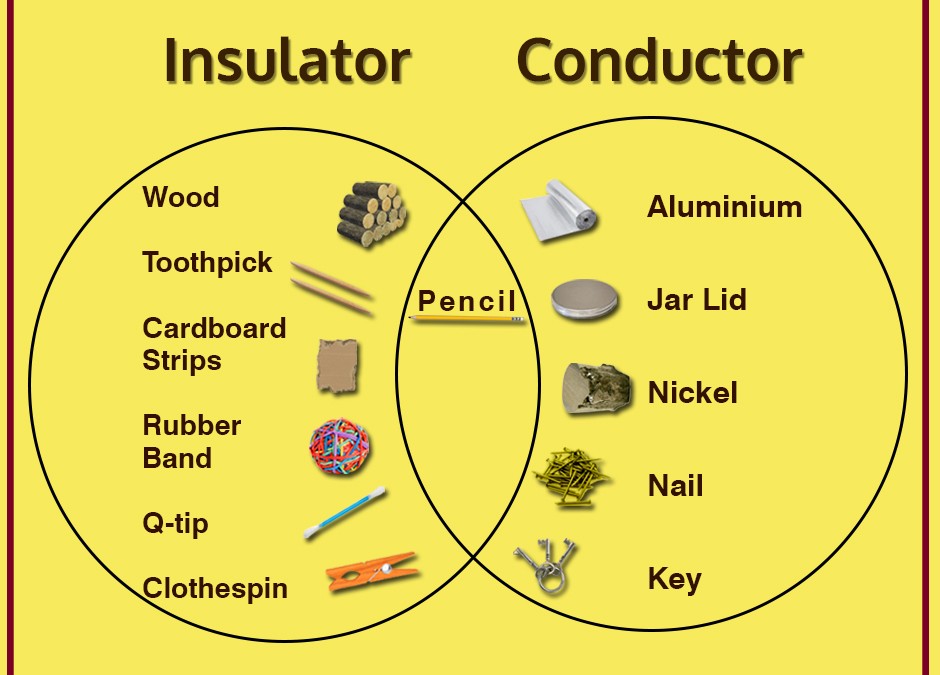
AboutTranscript. A conductor is a material that allows electrons to flow freely through it, making it useful for carrying electric current. An insulatoris a material that resists the flow of electrons, so it does not allow electric current to pass through it. Learn about how conductors and insulators work and how they are effected by changes in.

Conductors and Insulators Science Experiment Good conductor and bad conductor of electricity
A nonconductor of heat, such as wool, can be used to keep the body warm in cold weather. Because glass is a nonconductor, it is often used to insulate windows and prevent heat from escaping a building. The dry air in the desert is a nonconductor of electricity, which is why lightning strikes are less common in these areas.
PPT Physics 121 Electricity & Lecture 4 Gauss’s Law PowerPoint Presentation ID
: a nonconductor of direct electric current dielectric adjective Examples of dielectric in a Sentence Recent Examples on the Web In contrast, electrically insulating dielectric materials (stuff that doesn't conduct electricity well but does support electrostatic fields well) can withstand light fields thousands of times stronger.

What is Electricity? • Electricity • Physics Fox
The flow of electricity is called current. Metals are generally very good conductors, meaning they let current flow easily. Materials that do not let current flow easily are called insulators.
PPT Gauss’ Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5373915
noun a substance that does not readily conduct heat, sound, or electricity. Recommended videos Powered by AnyClip AnyClip Product Demo 2022 The media could not be loaded, either because the server or network failed or because the format is not supported. AnyClip Product Demo 2022 NOW PLAYING Feature Vignette: Live Feature Vignette: Management

The Importance Of Nonconductors In Electronics
Classes of Crystalline Solids. Crystalline substances can be described by the types of particles in them and the types of chemical bonding that take place between the particles. There are four types of crystals: (1) ionic, (2) metallic, (3) covalent network, and (4) molecular. Properties and several examples of each type are listed in the.

Electricity and Lighting SCIENCE IS LIFE
10 Electrical Insulators . Electric charges do not flow freely through insulators. This is an ideal quality in many cases—strong insulators are often used to coat or provide a barrier between conductors to keep electric currents under control. This can be seen in rubber-coated wires and cables. The most effective electrical insulators are:
Section 1 Electricity Nitty Gritty Science
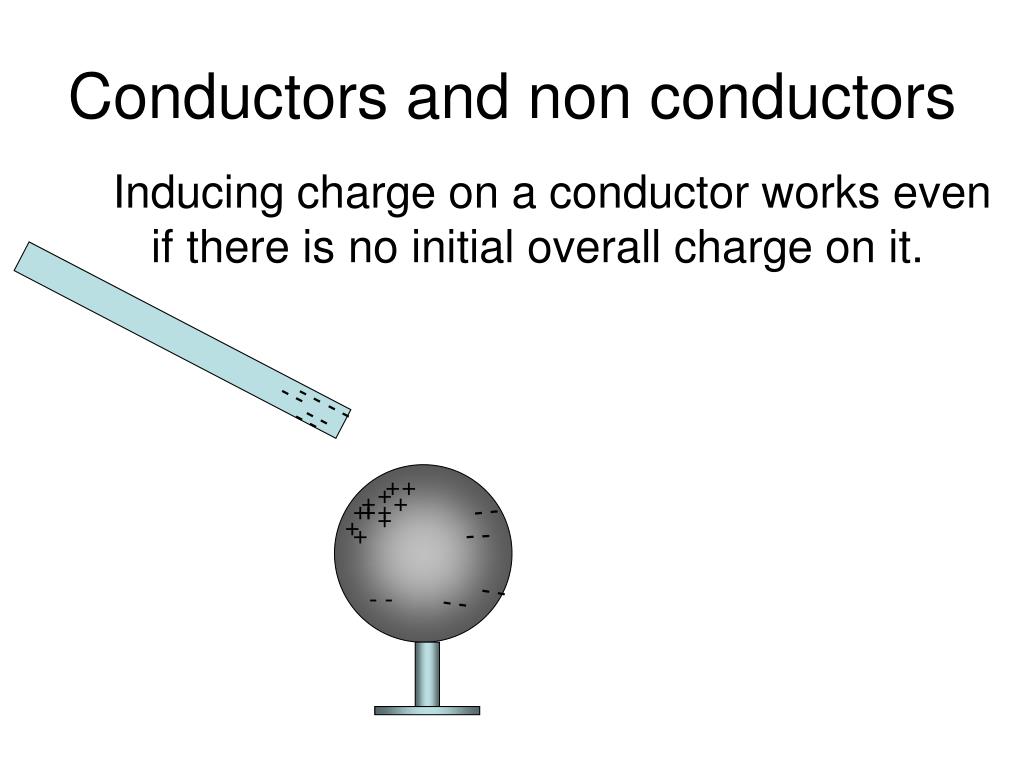
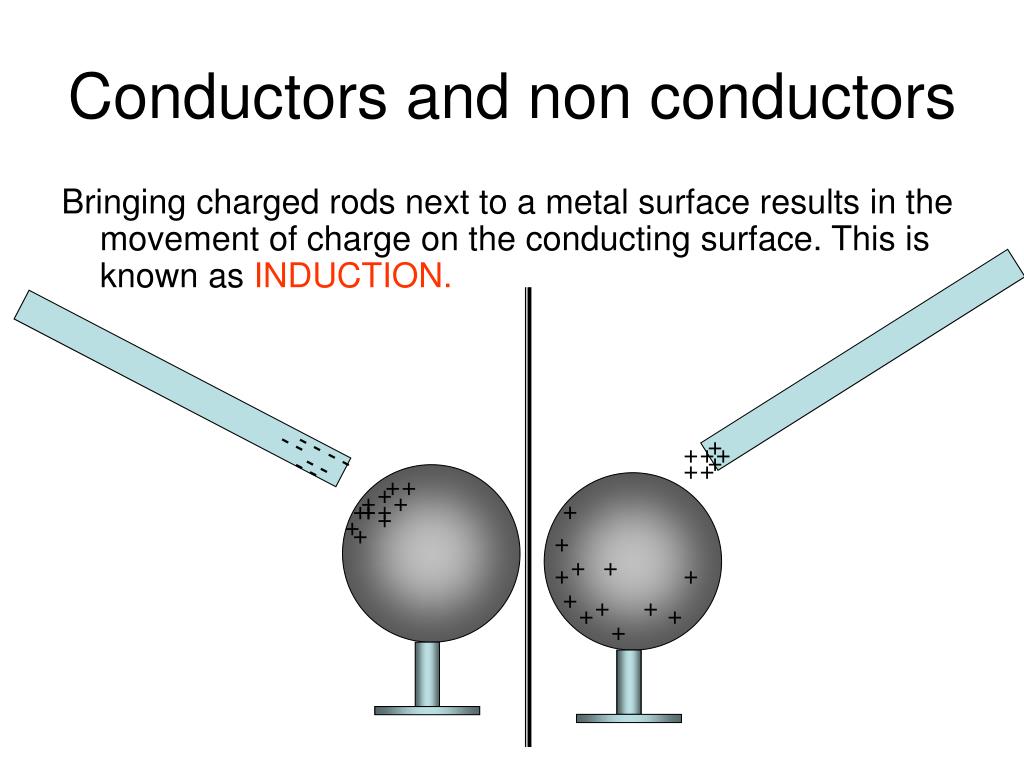
Figure 18.2.3 18.2. 3: Charging by induction. (a) Two uncharged or neutral metal spheres are in contact with each other but insulated from the rest of the world. (b) A positively charged glass rod is brought near the sphere on the left, attracting negative charge and leaving the other sphere positively charged.
Electricity 8th Grade science
Insulator Vs. Non-Conductor The primary distinction between an insulator and a non-conductor is that an insulator is any material that prevents heat, sound, or electricity from being transmitted. A non-conductor, on the other hand, is any substance that prevents the transfer of electricity.
Conductors Of Static Electricity
However, movement of electrical charges is much more constrained in nonconductors than in conductors. Electrons are allowed to move about in a conductor, and that is what allows the flow of electricity in a metal wire. In a nonconductor, the electrons are constrained within the atoms, so separation of charges particles does not work.

PPT Chapter 13 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6856680
Physical Properties of Metals. Metals are lustrous, malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity. Other properties include: State: Metals are solids at room temperature with the exception of mercury, which is liquid at room temperature (Gallium is liquid on hot days).; Luster: Metals have the quality of reflecting light from its surface and can be polished e.g., gold, silver and.